1 If limiting molar conductivity of Ca2+ and Cl– are 119.0 and 76.3 S cm2 mol-1, then the value of limiting molar conductivity of CaCl2 will be:
(a) 195.3 S cm2 mol-1
(b) 271.6 S cm2 mol-1
(c) 43.3 S cm2 mol-1
(d) 314.3 S cm2 mol-1
ANS: B
2 The emf of the cell:
Ni | Ni2+ (1.0 M) || Au3+ (1.0 M) | Au (E° = -0.25 V for Ni2+| Ni; E° = 1.5 V for Au3+| Au) is
(a) 1.25 V
(b) -1.25 V
(c) 1.75 V
(d) 2.0 V
ANS: C
3 The ratio of distance between electrodes and area of cross section is referred to as:
(a) Faraday’s constant
(b) Cell Constant
(c) Electrochemical equivalent
(d) Specific resistance
ANS: B
4 The conductance of electrolyte, when distance between electrodes is 1 cm and area of cross
section is 1 cm2 , is referred to as:
(a) Molar conductance
(b) Equivalent conductance
(c) Specific Conductance
(d) Specific Resistance
ANS: C
5 The standard emf of a galvanic cell involving cell reaction with n = 2 is formed to be 0.295 V at 25°C. The equilibrium constant of the reaction would be :
(a) 1.0 × 1010
(b) 2.0 × 1011
(c) 4.0 × 1012
(d) 1.0 × 102
[Given F = 96500 (mol-1 ); R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1]
ANS: A
6 An increase in molar conductance of a strong electrolyte with dilution is mainly due to:
(a) increase in both i.e. number of ions and ionic mobility of ions.
(b) Increase in number of ions
(c) increase in ionic mobility of ions
(d) 100% ionization of electrolyte at normal dilution
ANS: C
7 An increase in molar conductance of a weak electrolyte with dilution is mainly due to:
(a) increase in both i.e. number of ions and ionic mobility of ions.
(b) Increase in number of ions
(c) increase in ionic mobility of ions
(d) 100% ionization of electrolyte at normal dilution
ANS: A
8 The law that states that limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte can be represented as the sum of the individual contributions of the anion and cation of the electrolyte is known as:
(a) Faraday’s Law
(b) Kohlrausch’s law
(c) Avogadro’s Law
(d) Dalton’s law
ANS: B
9 A cathode and an anode are the most common components of an electrochemical cell. Which of the following claims about the cathode is correct?
a) Oxidation occurs at the cathode
b) Electrons move into the cathode
c) Usually denoted by a negative sign
d) Is usually made up of insulating material
ANS: B
10 Which of the following claims about electrochemical cells is true?
a) Cell potential is an extensive property
b) Cell potential is an intensive property
c) The Gibbs free energy of an electrochemical cell is an intensive property
d) Gibbs free energy is undefined for an electrochemical cell
ANS: B
11 Which of the following does not belong in the category of electrochemical cells?
a) Voltaic cell
b) Photovoltaic cell
c) Electrolytic cell
d) Fuel Cell
ANS B
12 The process of transmitting electric current through an electrolyte’s solution to decompose it is known as __________
a) Electrolyte
b) Electrode
c) Electrolysis
d) Electrochemical cell
ANS: C
13 Which of the following statements about a lead storage cell (or a lead-acid battery) is false?
a) It is a primary cell
b) The cathode is made up of lead(IV) oxide
c) The anode is made up of lead
d) The electrolyte used is an aqueous solution of sulphuric acid
ANS: A
14 The conductivity of electrolytic conductors is due to __________
a) Flow of free mobile electrons
b) Movement of ions
c) Either movement of electrons or ions
d) Cannot be considered
ANS: B
15 Effect of dilution on conductivity:
a) increases
b) decreases
c) remains same
d) none of the above
ANS: A
16 which of the following shows elelctrical conductance:
a) sodium
b) diamond
c) graphite
d) potassium
ANS: C
17 In a fuel cell, which of the following can be utilized as a fuel?
a) Nitrogen
b) Argon
c) Hydrogen
d) Helium
ANS: C
18 Which of the following is given to a fuel cell’s cathode?
a) Hydrogen
b) Nitrogen
c) Oxygen
d) Chlorine
ANS: C
19 The charge required for the reduction of 1 mol of MnO4– to MnO2 is
(a) 1 F
(b) 3 F
(c) 5 F
(d) 6 F
ANS: B
20 Ammonium nitrate is used in salt bridge because:
(a) it forms a jelly like material with agar-agar.
(b) it is a weak electrolyte.
(c) it is a good conductor of electricity.
(d) the transport number of NH4+ and NO3– ions are almost equal.
ANS: D
21 The reaction, 3ClO– (aq) → ClO3 (aq) + 2Cl– (aq) is an example of
(a) Oxidation reaction
(b) Reduction reaction
(c) Disproportionation reaction
(d) Decomposition reaction
ANS: C
22 Which of the following assertions about the main cell is correct?
a) An example of a primary cell is a mercury cell
b) An example of a primary cell is a nickel-cadmium storage cell
c) The electrode reactions can be reversed
d) It can be recharged
ANS A
23 Standard solution of KNO3 is used to make a salt bridge because:
(a) Velocity of K+ is greater than that of NO−3.
(b) Velocity of NO−3 is greater than that of K+.
(c) Velocity of both K+ and NO−3 are nearly same
(d) KNO3 is highly soluble in water.
ANS: C
24 Galvanised iron sheets are coated with:
(a) Carbon
(b) Copper
(c) Zinc
d) tin
ANS: C
25 How many coulombs are required for the oxidation of 1 mole of H2O to O2?
(a) 1.93 × 105 C
(b) 9.65 × 104 C
(c) 3.86 × 105 C
(d) 4.825 × 105 C
ANS: A
26 Rust is a mixture of:
(a) FeO and Fe (OH)3
(b) FeO and Fe (OH)2
(c) Fe2O3 and Fe (OH)3
(d) Fe3O4 and Fe (OH)3
ANS: C
27 The standard reduction potentials of Cu2+/Cu and Cu2+/Cu+ are 0.337V and 0.153 V respectively. The standard electrode potential of Cu+/Cu half cell is:
(a) 0.184 V
(b) 0.827 V
(c) 0.521V
(d) 0.490 V
ANS: C
28 In a dry cell, which of the following is the electrolyte?
a) Potassium hydroxide
b) Sulphuric acid
c) Ammonium chloride
d) Manganese dioxide
ANS: C
29 The volume of H2 gas at NTP obtained by passing 4 amperes through acidified H2O for 30 minutes is:
(a) 0.0836 L
(b) 0.0432 L
(c) 0.1672 L
(d) 0.836 L
ANS: A
A statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice from the
options given below:
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of
assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.
(E) assertion is false but reason is true
30 Assertion : The resistivity for a substance is its resistance when it is one meter long and its area of cross section is one square meter.
Reason : The SI units of resistivity is ohm metre ( m). ANS: B
31 Assertion : On increasing dilution, the specific conductance keep on increasing.
Reason : On increasing dilution, degree of ionisation of weak electrolyte increases and molality of ions also increases.
ANS: D
32 ASSERTION:Galvanised iron does not rust.
Reason : Zinc has a more negative electrode potential than iron.
ANS: A
33 Assertion : Current stops flowing when Ecell = 0.
Reason :
Equilibrium of the cell reaction is attained.
ANS: A
34 Assertion : A standard hydrogen electrode is also called reversible electrode.
Reason :
It can act on both as anode as well as cathode in an electrochemical cell.
ANS: A
35 . Assertion : Kohlrausch’s law helps to find the molar conductivity of weak electrolyte at
infinite dilution.
Reason :
Molar conductivity of a weak electrolyte at infinite dilution cannot be determined experimentally.
ANS: A
36 Assertion : When a copper wire is dipped in silver nitrate solution, there is no change in
the colour of the solution.
Reason :
Copper cannot displace silver from its salt solution.
ANS: D
37 . Assertion : Fluorine is the best oxidising agent.
Reason :
Fluorine has highest reduction potential.
ANS: A
38 Assertion:Electrolytic cell uses electrical energy to carry non-spontaneous chemical reactions.
Reason : Chemical energy of a spontaneous redox reaction can be converted into electrical energy.
ANS: B
39 Assertion :EMF of the cell is the potential difference between the electrode potentials of the cathode and anode when no current is drawn through the cell.
Reason: Anode is kept on the right side and cathode on the left side while representing the galvanic cell.
ANS: C
40 Assertion:A standard hydrogen electrode is also called irreversible electrode.
Reason : Standard hydrogen electrode can act both as anode as well as cathode in an electrochemical cell.
ANS: D
41 Assertion:Lithium has the lowest electrode potential.
Reason: Lithium ion is the strongest oxidising agent.
ANS:C
42 Assertion : To obtain maximum work from a galvanic cell charge has to be passed reversibly.
Reason: The reversible work done by a galvanic cell is equal to decrease in its Gibbs energy.
ANS: A
43 Assertion:Molar conductivity increases with decrease in concentration.
Reason:Conductivity always decrease with decrease in concentration.
ANS:B
44 Assertion:Kohlrausch law helps to find the molar conductivity of strong electrolyte at infinite dilution.
Reason:Molar conductivity of a strong electrolyte at infinite dilution cannot be determined experimentally.
ANS: D
45 Assertion:When a copper wire is dipped in silver nitrate solution, there is a change in the colour of the solution.
Reason : Copper cannot displace silver from its salt solution.
ANS: C
Zero
The arrangement of various elements in the order of increasing value of standard reduction potential is called Electrochemical Series.
Conductivity always decreases with a decrease in concentration, because the number of ions per unit volume that carry the current in a solution decreases on dilution.
The SI unit of conductance is Siemens, denoted by the symbol, S & is equal to Ω-1
Every conducting material offers some obstruction to the flow of electricity which is called resistance. Its unit is Ohm
The electronic conductance depends upon The nature and structure of the metal. The number of valence electrons per atom. Temperature (It is inversely proportional to temperature).
The molar conductivity of a solution at infinite dilution is called limiting molar conductivity and is represented by the symbol ΛmO.
(i) Fuel cells : These cells are the devices which convert the energy produced during combustion of fuels like H2, CH4, etc. directly into electrical energy. (ii) The molar conductivity of a solution at infinite dilution is called limiting molar conductivity and is represented by the symbol Λ°m.
Molar conductivity: Molar conductivity of a solution at a given concentration is the conductance of the volume ‘V’ of a solution containing one mole of electrolyte kept between two electrodes with area of cross section ‘A’ and distance of unit length. It is represented by Λm (lamda). Λm = KA/l , if I = 1 and A = V ∴ Λm = KV Unit = S cm2 mol-1 Secondary batteries : Those batteries which can be recharged by passing an electric current through them and can be used again and again are called secondary batteries.
(i) Mercury cell is used in hearing aids. (ii) Fuel cell was used in the Apollo Space Programme. (iii) Lead storage cell is used in automobiles and inverters. (iv) Dry cell does not have a long life.
46 Why is alternating current used for measuring the resistance of an electrolytic solution?
Ans: The alternating current keeps the concentration of ions constant whereas direct current changes the
concentration of ions. That is why alternating current used for measuring the
resistance of an electrolytic solution.
47 What is the potential of S.H.E.?
Ans: Zero
48 What is Electrochemical Series?
Ans: The arrangement of various elements in the order of increasing value of standard reduction potential
is called Electrochemical Series.
49 Conductivity of a solution decreases with increasing dilution of solution. Why?
Ans: Conductivity always decreases with a decrease in concentration, because the number of ions
per unit volume that carry the current in a solution decreases on dilution.
50 What does the positive value of standard electrode potential indicate?
Ans. The positive value of standard electrode potential indicates that the element gets reduced more
easily than ions and its reduced form is more stable than Hydrogen gas.
51 Give the unit of conductance?
Ans. The SI unit of conductance is Siemens, denoted by the symbol, S & is equal to Ω-1
52 State Kohlrausch’s Law?
Ans. Kohlrausch’s Law of independent migration of ion states that limiting molar
conductivity of an electrolyte can be represented as the sum of the individual
contributions of
the anion and cation of the electrolyte.
53 What is electrical resistance? What is its unit?
Ans: Every conducting material offers some obstruction to the flow of electricity which is called
resistance. Its unit is Ohm
54 What do you understand by strong and weak electrolytes? Give 2 examples of each.
Ans. An electrolyte that ionises completely in solution is a strong electrolyte e.g. NaCl, CaCl2 etc. and an electrolyte that ionizes partially in solution is weak electrolyte e.g.
CH3COOH, NH4OH.
55 The chemistry of corrosion of iron is essentially an electrochemical phenomenon. Explain the reactions occurring during the corrosion of iron in the atmosphere.
Answer:
The mechanism of corrosion is explained on the basis of electrochemical theory. By taking example of rusting of iron, we Refer tothe formation of small electrochemical cells on the surface of iron.
The redox reaction involves
At anode : Fe(S) —-> Fe2+ (aq) + 2e–
At cathode : H2O + CO2 ⇌ H2CO3 (Carbonic acid)
H2CO3 ⇌2H+ + CO32-
H2O ⇌ H+ + OH–
H+ + e– —-> H
4H + O2 —-> 2H2O
Then net resultant Redox reaction is
2Fe(s) + O2 (g) + 4H+ —-> 2Fe2+ + 2H2O
56 On what factors conductivity of electrolytic solution depends?
Ans: Electrolytic conductance depends upon the nature of the electrolyte added, the size of ions
produced and their solutions, the nature of the solvent and its viscosity, concentration of the
electrolyte and temperature. (directly proportional to temperature).
57 E° values for Fe3+/Fe2+ and Ag+ /Ag are respectively 0.771 V and 0.800 V. Is the reaction:
Fe3+ + Ag → Fe2+ + Ag+
spontaneous or not?
Ans:E° for the reaction is 0.771 – 0.800 = – 0.029 V. Therefore, the reaction is not
spontaneous
58 How is standard electrode potential of a cell related to? 2
i) Equilibrium constant? ii) Gibbs free energy change.
Ans. (i) Standard electrode potential and equilibrium constant
E°cell = 0.0591 log Kc
ΔrG° = -nFE°
59 The conductivity of an aqueous solution of NaCl in a cell is 92 Ω-1 cm-1 the resistance offered by this
cell is 247.8Ω. Calculate the cell constant.
Ans. Specific conductivity = 𝐶𝑒𝑙𝑙 𝐶𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡 / resistance
Or Cell constant = Conductivity × Resistance
= 92Ω-1 cm-1 × 247.8Ω = 22797.6 Ω-1
60 The conductivity of metals decreases while that of electrolytes increases with increases in
temperature. Why?
Ans. With increase in temperature, the K.E. of metal cation increases and obstructs the free flow of
electrons decreasing the conducts of metal while in case of electrolytes, increased
temperature increases the mobility of ions this increases the conductance of ions.
61 In fig. below, identify the nature of electrolyte A& B. In which case it is not possible to obtain value of limiting molar conductance?
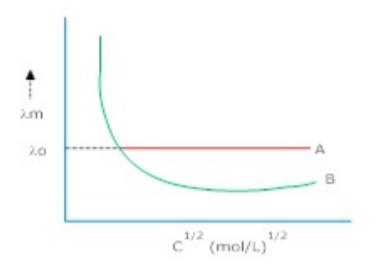
Ans. A = strong electrolyte, B = weak electrolyte. In case of B, it is not possible to get an
exact value of limiting molar conductance.
62 The conductivity of 0.20 M solution of KCl at 298 K is 0.0248Scm-1 . Calculate its molar
conductivity.
Ans. Given,
𝜅 = 0.0248Scm-1
124 S cm2mol-1
63 Represent the galvanic cell in which the following reactions take place
Zn(s) + 2Ag+ (aq) → Zn2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
i.) Which one of the electrodes is negatively charged?
ii.) Write the reaction taking place at each of the electrodes.
iii.) Name the carrier of current within the cell.
Ans .The cell is represented as
Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq) || Ag+ (aq) | Ag(s)
i) Zn electrode is negatively charged
ii) At anode
Zn(s) → Zn2+ + 2e–
At cathode
Ag+ (aq) + e– → Ag(s)
iii) Ions are the carrier of current within the cell.
64 What are the factors on which electronic conductance depends?
Ans: The electronic conductance depends upon
The nature and structure of the metal.
The number of valence electrons per atom.
Temperature (It is inversely proportional to temperature).
65 For what concentration of Ag+ (aq) will the emf of the given cell be zero at 25°C if the
concentration of Cu2+is 0.1 M ?
Cu(s) | Cu2+ (0.1M) || Ag+ (aq) | Ag(s) ; E°Ag+/Ag = 0.80V; E°Cu2+/Cu = 0.34V
Ans.[Ag+ ] = 5.3 X 10 -9M
66 What is the cell potential for the cell at 250C,
Cr |Cr3+(0.10) || Fe2+(0.01) | Fe
E°Cr3+/Cr = -0.74V; E°Fe2+/Fe = -0.44V
Ans.The cell reaction is 2Cr + 3Fe2+ + 6e- → 2Cr3+ + 3Fe
67 What is meant by ‘limiting molar conductivity’?
Answer:
The molar conductivity of a solution at infinite dilution is called limiting molar conductivity and is represented by the symbol ΛmO.
68 Two half-reactions of an electrochemical cell are given below :
MnO–4 (aq) + 8H+ (aq) + 5e– —–> Mn2+ (aq) + 4H2O (I), E° = 1.51 V
Sn2+ (aq) → Sn4+ (aq) + 2e–, E° = + 0.15 V.
Construct the redox reaction equation from the two half-reactions and calculate the cell potential from the standard potentials and predict if the reaction is reactant or product favoured.
Answer:
The reactions can be represented at anode and at cathode in the following ways :
At anode (oxidation) :
Sn2+ (aq) → Sn4+ (aq) + 2e–, E° = + 0.15 V.
Af cathode (reduction) :
MnO–4 (aq) + 8H+ (aq) + 5e– —–> Mn2+ (aq) + 4H2O (I), E° = 1.51 V
The Net R × M = 2MnO–4(aq) + 16H+ + 5Sn2+ —–> 2Mn2+ + 5Sn4+ + 8H2O
Now E°cell = E°cathode – E°anode
= 1.51 – 0.15 = + 1.36 V
∴ Positive value of E°cell favours formation of product.
69 Express the relation among cell constant, resistance of the solution in the cell and conductivity of the solution. How is molar conductivity of a solution related to its conductivity?
Answer:
GG* = K
where Q is conductance;
G * is cell constant;
K is conductivity
G* × 1R = K ⇒ G* = RK
∴ Λm = K×1000C S cm2 mol-1
70 The molar conductivity of a 1.5 M solution of an electrolyte is found to be 138.9 S cm2 mol-1. Calculate the conductivity of this solution.
Answer:
C = 1.5 M, Λm = 138.9 S cm2 mol-1
Λm = K×1000 / c
∴K = Λm×C1000=138.9×1.51000 = 0.20835 S cm-1
71 The conductivity of 0.001 M acetic acid is 4 × 10-5 S/cm. Calculate the dissociation constant of acetic acid, if molar conductivity at infinite dilution for acetic acid is 390 S cm2/mol.
Answer:
Given : K = 4 × 10-5 S/cm, M = 0.001 M
Λ°m = 390 S cm2/mol, k = ?
Using the formula
![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
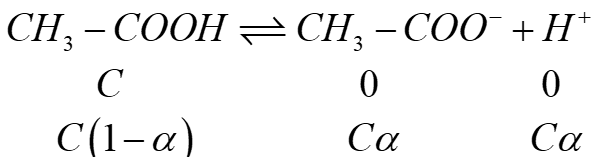
![]()
= ![]()
![]()
= ![]()
k = 1.46 × 10-6
72 The standard electrode potential for Daniell cell is 1.1 V. Calculate the standard Gibbs energy for the cell reaction. (F = 96,500 C mol-1)
Answer:
Given : E° = 1.1V, F = 96,500 C mol–, n = 2
Zn + Cu2+ —–>⇌ Cu + Zn2+
Using ΔG° = -nFE° = -2 × 96500 × 1.1
212300
73 State Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions. Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution?
Answer:
Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions: The limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte (i.e. molar conductivity at infinite dilution) is the sum of the limiting ionic conductivities of the cation and the anion each multiplied with the number of ions present in one formula unit of the electrolyte.
Λ°m for AxBy = xλ°+ + yλ°–
For acetic acid Λ° (CH3COOH) = λ°CH3COO– + λ°H+
Λ°(CH3COOH) = Λ° (CH3COOK) + Λ° (HCl) – Λ° (KCl)
74 Define the following terms :
(i) Fuel cell
(ii) Limiting molar conductivity (Λ°m)
Answer:
(i) Fuel cells : These cells are the devices which convert the energy produced during combustion of fuels like H2, CH4, etc. directly into electrical energy.
(ii) The molar conductivity of a solution at infinite dilution is called limiting molar conductivity and is represented by the symbol Λ°m.
75 Define the following terms :
(i) Molar conductivity (Λm)
(ii) Secondary batteries
Answer:
Molar conductivity: Molar conductivity of a solution at a given concentration is the conductance of the volume ‘V’ of a solution containing one mole of electrolyte kept between two electrodes with area of cross section ‘A’ and distance of unit length. It is represented by Λm (lamda).
Λm = KA/l , if I = 1 and A = V
∴ Λm = KV Unit = S cm2 mol-1
Secondary batteries : Those batteries which can be recharged by passing an electric current through them and can be used again and again are called secondary batteries.
76 Set up Nemst equation for the standard dry cell. Using this equation show that the voltage of a dry cell decreases with use..
Answer:
Cell reaction of a dry cell can be represented as
Zn + Hg2+ → Zn2+ + Hg (n = 2)
Nemst equation
Ecell = E°cell – 0.05912log[Zn2+]/Hg2+
The voltage of dry cell has to decrease because the concentration of electrolyte decreases in the reactions.
77 Define conductivity and molar conductivity for the solution of an electrolyte. Discuss their Variation with change in temperature.
Answer:
Conductivity: Conductivity of a solution is defined as the conductance of a solution of 1 cm length and having 1 sq. cm as the area of cross-section. It is represented by K.
Its unit is S cm-1
Molar conductivity : Molar conductivity of a solution at a dilution V is the conductance of all the ions produced from one mole of the electrolyte dissolved in V cm3 of the solution when the electrodes are 1 cm apart and the area of the electrodes is so large that the whole of the solution is contained between them. It is represented by Λm.
Its unit is S cm2 mol-1
Conductivity and molar conductivity of electrolytes increase with increasing temperature.
78 Calculate the time to deposit 1.27 g of copper at cathode when a current of 2A was passed through the solution of CuSO4.
(Molar mass of Cu = 63.5 g /mol,1 F = 96500 C/ mol)
Answer:
CuSO4 → Cu+2 + SO42-
Cu2+ + 2e– ——> Cu
63.5 gram of copper is deposited = 2 × 96500 C
1.27 gram of Cu is deposited = 2×9650063.5 × 1.27
= I × t (Q = I × t)
t = 2×96500×1.2763.5×2 = 1930 seconds
79 From the given cells: Lead storage cell, Mercury cell, Fuel cell and Dry cell
Answer the following:
(i) Which cell is used in hearing aids?
(ii) Which cell was used in Apollo Space Programme?
(iii) Which cell is used in automobiles and inverters?
(iv) Which cell does not have long life?
Answer:
(i) Mercury cell is used in hearing aids.
(ii) Fuel cell was used in the Apollo Space Programme.
(iii) Lead storage cell is used in automobiles and inverters.
(iv) Dry cell does not have a long life.
80 Calculate the degree of dissociation of acetic acid if its molar conductivity (Λm) is 39.05 S cm2 mol-1.
Given: λ°(H+) = 349.6 S cm2 mol-1 and λ°(CH3COO–) = 40.9 S cm2 mol-1.
Answer:
Λ°m(HAC) = λ°H+ + λ°AC–
= λ°CH3COOH = λ°H+ + λ°CH3COO–
349.6 S cm2 mol-1 + 40.9 S cm2 mol-1
390.5 S cm2 mol-1
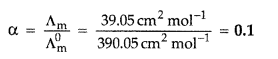
81 Write the name of the cell which is generally used in hearing aids. Write the reactions taking place at the anode and the cathode of this cell.
Answer:
Mercury cells are used in hearing aids.
Reaction at anode:
Zn (Hg) + 2OH– —–> ZnO (s) + H2O + 2e–
Reaction at cathode:
HgO + H2O + 2e– —–> Hg (l) + 2OH–
82 Write the name of the cell which is generally used in inverters. Write the reactions taking place at the anode and the cathode of this cell.
Answer:
Lead storage battery is used in inverters.
At Anode:
Pb(s) + SO2−4(aq) —–> PbSO4 (s) + 2e–
At Cathode:
PbO2(s) + SO2−4(aq) + 4H+ (aq) + 2e–
PbSO4 (s) + 2H2O
83 On the basis of their standard electrode potential values, which reaction is feasible at cathode and why?
![]()
![]()
Answer:
Since the standard electrode potential of Cu2+ is greater than that of H+, so reaction (i) will be feasible at cathode.
i.e. Cu2+(aq) + 2e —–> Cu
Cu2+ has higher reduction potential.
84 How many coulombs are required to reduce 1 mole Cr2O72- to Cr3+?
(b) The conductivity of 0.001 M acetic acid is 4 × 10-5 S/m. Calculate the dissociation constant of acetic acid if Λ0m,for acetic acid is 390 S cm 2 mol.-1
Answer:
(a) Cr2O7-2 + 14H+ + 6e —-> 2Cr-3 + 7H2O
∴ 6 Faraday of charge is required
(b) Conductivity (K) = 4 × 10-5 S / cm
Concentration (C) = 0.001M
Molar Conductivity ![]()
![]()
= 40 S cm2 mol-1
Degree of dissociation ![]()
![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
=1.158 × 10-5
85 The cell in which the following reaction occurs :
2Fe3+ (aq) + 2I– (aq) → 2Fe2+ (aq) + I2 (s) has E0cell = 0.236V at 298K. Calculate the standard Gibbs energy and the equilibrium constant of the cell reaction.
(Antilog of 6.5 = 3.162 × 106; of 8.0 = 10 × 108; of 8.5 = 3.162 × 108)
Answer:
log KC = nE0 cell 0.0591=2×0.2360.0591 = 8
KC = antilog 8 = 1 × 108
ΔG° = -nFE0cell = -2 × 96500 × 0.236
-45548 J/mol-1
86 Calculate the emf of the following cell at 298 K: Fe(s) | Fe2+ (0.001 M) || H+ (1M) | H2(g) (1 bar), Pt(s) (Given E°cell = +0.44V) .
Answer:
As Fe + 2H+ —-> Fe2+ + H2 (n = 2)
According to Nernst equation
![]()
![]()
![]()
= 0.44 + 0.0887 = 0.529 V
87 Can E0cell or ΔrG0 for a cell reaction ever be equal to zero. Why or why not?
Solution: No, it cannot be equal to zero for a cell reaction proceeding in a particular direction (forward or backward direction)
88 Under what conditions is E0cell = 0 and ΔrG0 = 0 ?
Solution: At the condition of equilibrium, E0cell = 0 and ΔrG0 = 0
89 What does the negative sign in the expression E0Zn2+ /Zn = – 0.76 V means?
Solution: It implies that Zn is more reactive than hydrogen or it is a stronger reducing agent. In a cell containing zinc electrode and standard hydrogen electrode present in two half cells, zinc will be oxidised to Zn2+ ions while H+ ions will get reduced to hydrogen.
90 Aqueous copper sulphate solution and aqueous silver nitrate solution are electrolysed by 1 ampere current for 10 minutes in separate electrolytic cells. Will the mass of copper and silver deposited on the cathode be same or different? Explain your answer.
ANSWER: It will be different. According to Faraday’s second law, the amounts of different substances liberated by the same quantity of electricity passing through the electrolytic solution are proportional to their chemical equivalent weights No. of electronsAtomic mass of metal electrons required to reduce the cation.
Hence, one mole of Cu2+ and Ag+ require 2 mol of electron (2F) and 1 mol of electrons (1F) respectively.
91 How much copper will be deposited at cathode by passing 5 ampere electricity through CuSO4 solution for 45 minutes?
ANSWER: n = 180 X 45 / 96500 X 2
0.041 moles ==> 0.041 X 63.5 = 2..6 gm
92 2.47g of CuO was obtained by oxidising 1.986g of copper by nitric acid. 0.335g copper was precipitated by 0.346g of zinc from CuSO4 solution. What are the equivalent weight of copper and zinc respectively:
Equivalent mass of Cu=Mass of oxygen in oxideMass of Metal×8 Given
(2.47−1.986)1.986×8=32.82 MCuo=2.47g
MCu=1.986g
Now, Mass of CuMass of Zn=Eq. mass of CuEq. mass of Zn
∴ Eq. mass of Zn=33.89
93 How will the pH of brine (aq. NaCl solution) be affected when it is electrolyzed?
ANSWER: There is formation of sodium hydroxide which is a strong base. And bases have generally greater value of pH.
Hence, the pH will be increased during the electrolysis of brine solution.
94 Can an electrochemical cell acts as electolytic cell. Explain.
ANSWER: Yes, by passing external electric poential greater than own electric ptential.
95 What does positive value of an standard electrode potential indicate?
ANSWER: The element casn reduce more easily than hydrogen. And its reduced form is more stablle than hydrogen gas.
96 Write the Nernst equation for the cell reaction in the Daniell cell. How will the Ecell be affected when concentration of Zn2+ ions is increased ?
Solution: Daniell cell involves the redox reaction :
Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu(s)
Thus in the cell Zn(s) is oxidised to Zn²+ (aq) ions in the oxidation half cell while Cu²+ (aq) ions are reduced to Cu(s) in the reduction half cell.
According to Nernst equation,
Ecell = E0cell – (0.059/2) {log[Zn2+(aq)] / [Cu2+(aq)]
Hence Ecell decreases as the [Zn2+(aq)] increases.
97 What advantage do the fuel cells have over primary and secondary batteries?
Solution: Primary batteries or cells contain a limited amount of reactants and are discharged when the reactants are consumed. Secondary batteries or cells can be recharged but the process takes a long time. Fuel cells work continuously as long the reactants (i.e. fuel) are supplied.
98 Match the terms given in Column I with the units given in Column II.
Column I Column II
(a) Λm (i) S cm-1
(b) Ecell (ii) m-1
(c) C (iii) S cm2 mol-1
(d) G* (iv) V
Solution: (a) – (iii); (b) – (iv); (c) – (i); (d) – (ii)
99 Match the items of Column I and Column II.
Column I Column II
(a) Lead storage battery (i) maximum efficiency
(b) Mercury cell (ii) prevented by galvanisation
(c) Fuel cell (iii) gives steady potential
(d) Rusting (iv) Pb is anode, PbO₂ is cathode
Solution: (a) – (iv); (b) – (iii); (c) – (i); (d) – (ii)
100 Match the items of Column I and Column II.
Column I Column II
(a) c (i) I x t
(b) Λm (ii) Λm / Λ0m
(c) α (iii) k/c
(d) Q (iv) G*/R
Solution: (a) – (iv); (b) – (iii); (c) – (ii); (d) – (i)
101 Match the items of Column I and Column II. (Any four)
Column I Column II
(a) Lechlanche cell (i) cell reaction 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
(b) Ni-Cd cell (ii) does not involve any iron in solution and is used in hearing aids.
(c) Fuel cell (iii) rechargeable
(d) Mercury cell (iv) reaction at anode, Zn → Zn2+ + 2e–
(e) converts energy of combustion into electrical energy.
Solution: (a) – (iv); (b) – (iii); (c) – (i), (d) – (ii), (e) (i)
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
102 Electrolysis is the process in which electricity is passed through a solution containing electrolytes. The decomposition of material occurs at the cathode when chemical reactions in the solution occur. The products of electrolysis are atoms, molecules, ions or gases.Products of electrolysis depend on the material being electrolyzed,on the nature of electrodes too,Various oxidising and reducing species present in the electrolytic cell If sodium chloride is melted (above 801o C), two electrodes are inserted into the melt, and an electric current is passed through the molten salt, then chemical reactions take place at the electrodes. Since the electrolyte is molten Sodium Chloride we only have Na + and Cl − ions in the solution.
Sodium ions migrate to the cathode, where electrons enter the melt and are reduced to sodium metal
Based on above paragraph , answer the following questions::
a) write the products obtained on electrolysis of molten NaCl.
b) write the products obtainned on electrolysis of aqueous NaCl.
c) In electrolysis of aqueous NaCl using platinum electrode, name the gas liberated at cathode.
ANS: A) Na, Cl2,, B) H2, O2, C) O2
103 Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Molar conductivity of ions are given as product of charge on ions to their ionic mobilities and Faraday’s constant.
For electrolytes say AXBy, molar conductivity is given by
λm(AxBy)=xnμAn+F+ymλAm−F
Ions Ionic mobility
K+ 7.616 x 10- 4
Ca2+ 12.33 x 10-4
Br– 8.09 x 10- 4
SO42− 16.58 x 10– 4
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer
(i) At infinite dilution, the equivalent conductance of CaSO4 is
(a) 256 x 10-4 B) 279 C) 23.7 D) 2x 10-8
(ii) If the degree of dissociation of CaSO4 solution is 10% then equivalent conductance of CaSO4 is
(a) 3.59 B) 36.9 C) 27.9 D) 30.6
(iii) What is the unit of equivalent conductivity?
(a) ohm-1 cm2 eq-1 B) ohm cm2 eq-1
(c) ohm-1 cm eq-1 d) ohm cm2 eq-1
(iv) If the molar conductance value of Ca2+ and Cl– at infinite dilution are 118.88 x 10-4 m2 mho mol-1 and 77.33 x 10-4 m 2 mho /mol respectively then the molar conductance of CaCl2 (in m2 mho /mol) will be
(a) 120.18 x 10– 4 b) 135 X 10 -4 c) 275.54 X 10 -4 d) 192.1 X 10 -4
ANS: I) B , II) C III) A IV) C
104 Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Standard electrode potentials are used for various processes:
(i) It is used to measure relative strengths of various oxidants and reductants.
(ii) It is used to calculate standard cell potential.
(iii) It is used to predict possible reactions.
A set of half-reactions (in acidic medium) along with their standard reduction potential, Eo (in volt) values are given below
I2+2e−→2I−;E∘=0.54
Cl2+2e−→2Cl−;E∘=1.36
Mn3++e−→Mn2+;E∘=1.50
Fe3++e− —–>Fe2+;E∘=0.77
O2+4H++4e− —–> 2H2O;E∘=1.23
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
(i) Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) CI– is oxidised by O2 (b) Fe2+ is oxidised by iodine
(c) I– is oxidised by chlorine. (d) Mn2+ is oxidised by chlorine
(ii) Mn3+ is not stable in acidic medium, while Fe3+is stable because
(a) O2 oxidises Mn2+ to Mn3+
(b) O2 oxidises both Mn2+ to Mn3+ and Fe2+ to Fe3+
(c) Fe3-oxidises H2O to O2
(d) Mn3+ oxidises H2O to O2
(iii) The strongest reducing agent in the aqueous solution is
(a) I– B) Cl– c) Mn+2 d) Fe+2
(iv) The emf for the following reaction is
I2+KCl —-> ⇌2KI + Cl2
(a) -0.82 V B) + 0.82V C) -0.73V D) +0.73V
ANS: I) B II) B III) A IV) A
105 Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :
All chemical reactions involve interaction of atoms and molecules. A large number of atoms/molecules are present in a few gram of any chemical compound varying with their atomic/molecular masses. To handle such large number conveniently, the mole concept was introduced. All electrochemical cell reactions are also based on mole concept. For example, a 4.0 molar aqueous solution of NaCI is prepared and 500 mL of this solution is electrolysed. This leads to the evolution of chlorine gas at one of the electrode. The amount of products formed can be calculated by using mole concept.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer :
(i) The total number of moles of chlorine gas evolved is :
(a) 0.5 b) 1.0 c) 1.5 d) 1.9
(ii) If cathode is a Hg electrode, then the maximum weight of amalgam formed from this solution is:
(a) 300 g b) 446g c) 396 gm d) 296gm
(iii) In the electrolysis, the number of moles of electrons involved are:
(a) 2 b) 1 c) 3 d) 4
(iv) In electrolysis of aqueous NaCl solution when Pt electrode is taken, then which gas is liberated at cathode?
(a) H2 gas b) Cl2 gas c) O2 gas d) none of these
ANS: I) B II) C III) B IV) A
