Define the term ‘order of reaction’ for chemical reactions.
The sum of powers of the concentrations of the reactants in the rate law expression is called the order of reaction.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound:
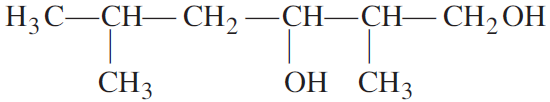
Ans 2, 5-Dimethyl hexane-1, 3-diol.
Arrange the following compounds in an increasing order of their acid strengths:
(CH3)2CHCOOH, CH3CH2CH(Br)COOH, CH3CH(Br)CH2COOH
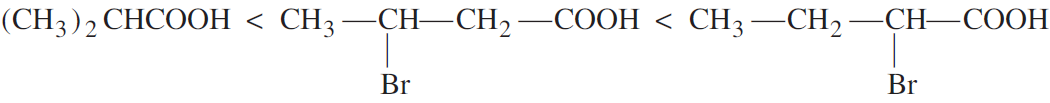
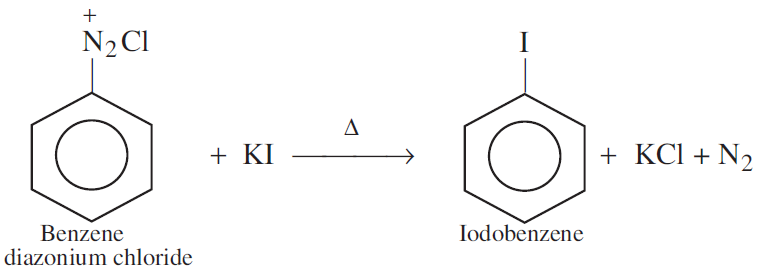
Write a chemical reaction in which the iodide ion replaces the diazonium group in a diazonium salt.
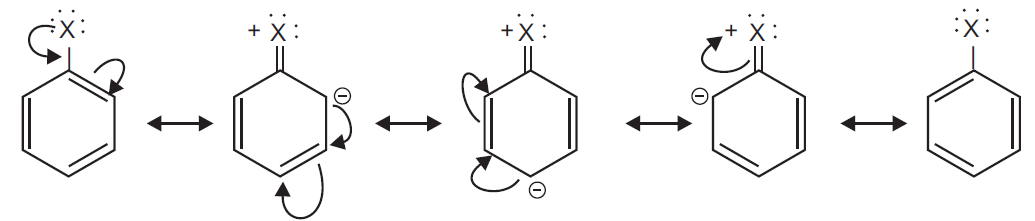
Explain as to why haloarenes are much less reactive than haloalkanes towards nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Ans In haloarenes C—X bond acquires a partial double bond character due to resonance. As a result the bond cleavage in haloarenes is difficult than haloalkanes and therefore, they are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction.
State Henry’s law correlating the pressure of a gas and its solubility in a solvent and mention two applications of the law.
It states that at constant temperature the mass of a gas(m) dissolved in a given volume of the liquid is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas () Ppresent in equilibrium with the liquid.
Mathematically, m∝ P or m = KHP where KH is the Henry’s law constant.
Applications of Henry’s law are
(i) To increase the solubility of CO2 in soft drinks and soda water, the bottle is sealed under high pressure.
(ii) To minimize the painful effects accompanying the decompression of deep sea divers, oxygen diluted with less soluble helium gas is used as breathing gas.
Define the following terms in relation to proteins: (i) Peptide linkage (ii) Denaturation
(i)Peptide linkage: A peptide linkage is an amide linkage (-CONH-) formed between -COOH group of one α-amino acid and NH2 group of the other amino acid by the elimination of a water molecule.
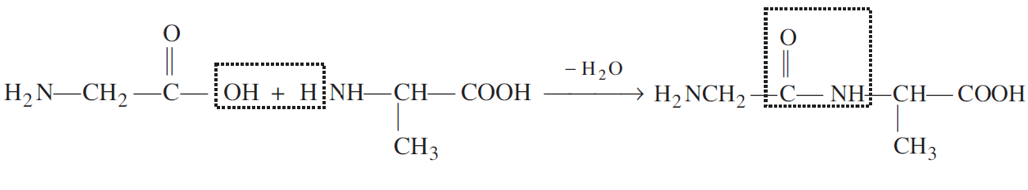
(ii) Denaturation: When a protein in its native form is subjected to physical change like change in temperature or chemical change like change in pH, the hydrogen bonds are disturbed. Due to this, globules unfold and helix get uncoiled and proteins loses its biological activity. During denaturation 2° and 3° structures of proteins are destroyed but 1° structure remains intact, e.g., coagulation of egg white on boiling.
What is a ligand? Give an example of a bidentate ligand.
The ion, atom or molecule bound to the central atom/ion in the coordination entity is called ligand. A ligand should have lone pair of electrons in their valence orbital which can be donated to central metal atom/ion.
Bidentate ligand: ![]() (Ethylene diamine)
(Ethylene diamine)
Name the reagents which are used in the following conversions: (i) A primary alcohol to an aldehyde (ii) Butan-2-one to butan-2-ol (iii) Phenol to 2, 4, 6-tribromophenol
(i) Pyridinium chlorochromate ![]() or Cu/573 K
or Cu/573 K
(ii) LiAlH4 / ether
(iii) Br2/H2O
Assign reasons for the following:
(i) The enthalpies of atomisation of transition elements are high.
(ii) The transition metals and many of their compounds act as good catalysts.
(iii) From element to element the actinoid contraction is greater than the lanthanoid contraction.
(iv) The E° value for the Mn3+ / Mn2+ couple is much more positive than that of Cr3+ / Cr2+.
(v) Scandium (Z = 21) does not exhibit variable oxidation states and yet it is regarded as a transition element.
(i) This is because transition metals have strong metallic bonds as they have a large number of unpaired electrons.
(ii) The catalytic activity of transition metals is attributed to the following reasons:
(a) Because of their variable oxidation states transition metals form unstable intermediate compounds and provide a new path with lower activation energy for the reaction.
(b) In some cases, the transition metal provides a suitable large surface area with free valencies on which reactants are adsorbed.
(iii) This is due to poorer shielding by 5f electrons in actinoids than that by 4f electron in the lanthanoids.
(iv) This is because half filled d-subshell (3d5) in Mn2+ is more stable.
(v) This is because scandium has partially filled d orbitals in the ground state (3d14s2).
Describe the following reactions: (i) Cannizaro reaction (ii) Cross aldol condensation
(i) Cannizzaro reaction: Aldehydes which do not have an α-hydrogen, undergo self oxidation and reduction (disproportionation) reaction on treatment with concentrated alkali. In this reaction one molecule of the aldehyde is reduced to alcohol while another is oxidised to carboxylic acid salt.
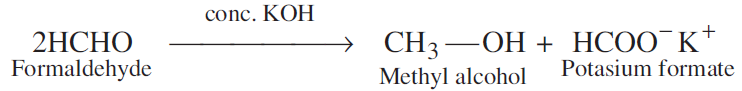
(ii) Cross aldol condensation: When aldol condensation is carried out between two different aldehydes and/or ketones, it is called cross aldol condensation.
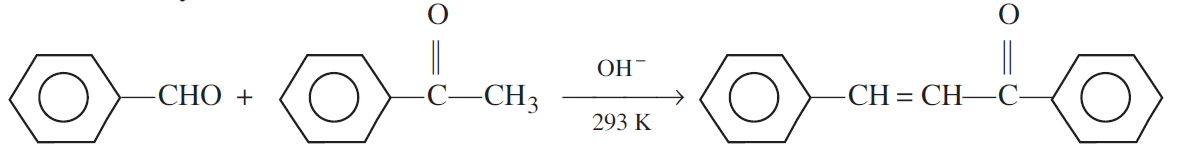
If both of them contain α-hydrogen atoms. It gives a mixture of four products.
State Raoult’s law for solutions of volatile liquids. Taking suitable examples explain the meaning of positive and negative deviations from Raoult’s law.
Raoult’s law: It states that for a solution of volatile liquids the partial pressure of each component is directly proportional to its mole fraction. Mathematically
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Positive deviation from Raoult’s law: In this type of deviation the partial pressure of each component of solution is greater than that calculated from Raoult’s law, i.e., ![]() &
& ![]()
Example: A solution of water and ethanol.
Negative deviation from Raoult’s: In this type of deviation the partial pressure of each component of solution is less than that expected from Raoult’s law, i.e., ![]() &
& ![]()
Example: A solution of acetone and chloroform.
Define the term osmotic pressure. Describe how the molecular mass of a substance can be determined by a method based on measurement of osmotic pressure?
Osmotic pressure (π) defined as the extra pressure that must be applied to the solution side in order to prevent the flow of solvent molecules into it through a semipermeable membrane.
![]()
where V is the volume of solution in litres containing nB moles of the solute. If WB grams of the solute whose molecular mass MB is present in the solution then
![]()
Thus, knowing WB,T, π and V molecular mass of the solute, MB can be calculated.
