Monochlorination of toluene in sunlight followed by hydrolysis with aq. NaOH yields.
(i) o-Cresol (ii) m-Cresol
(iii) 2, 4-Dihydroxytoluene (iv) Benzyl alcohol
Ans (iv) Benzyl alcohol
The process of converting alkyl halides into alcohols involves ___________.
(i) addition reaction (ii) substitution reaction
(iii) dehydrohalogenation reaction (iv) rearrangement reaction
Ans (ii) substitution reaction
IUPAC name of m-cresol is ___________.
(i) 3-methylphenol (ii) 3-chlorophenol
(iii) 3-methoxyphenol (iv) benzene-1,3-diol
Ans (i) 3-methylphenol
Which of the following compounds will react with sodium hydroxide solution in water?
(i) C6H5OH (ii) C6H5CH2OH (iii) (CH3)3COH (iv) C2H5OH
Ans (i) C6H5OH
Which of the following is most acidic?
(i) Benzyl alcohol (ii) Cyclohexanol (iii) Phenol (iv) m-Chlorophenol
Ans (iv) m-Chlorophenol
The C-O-C bond angle in the ether molecule is :
(a) 101° (b) 90° (c) 120° (d) 180º
Ans. (a)
Which of the following reagents will not convert ethyl alcohol into ethyl chloride ?
(a) PCl5 (b) NaCl (c) SOCl2 (d) HCl/ZnCl2
Ans. (b)
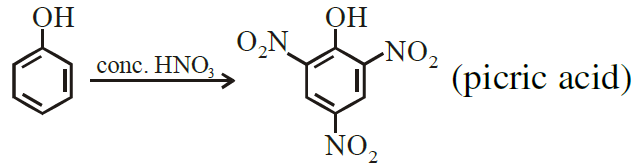
Phenol on being heated with concentrated H2SO4 and then with concentrated HNO3 gives:
(a) o-nitrophenol (b) 2,4,6-trinitrophenol
(c) p-nitrophenol (d) m-nitrophenol
Ans. (b)
Major products formed by heating (CH3)3C.O.CH2.CH3 with HI are:
(a) (CH3)3C.I and CH3CH2OH (b) (CH3)3C.OH and CH3CH2I
(c) (CH3)3C.I and CH3CH2I (d) (CH3)3C.OH and CH3CH2OH
Ans. (a)
In the following reaction: CH3-Br ![]() X
X ![]() Y
Y
‘Y’ will be :
(a) CH4 (b) CH3MgBr (c) CH3.OH (d) CH3.CH3
Ans. (a)
Phenol is more acidic than ethanol because :
(a) Ethoxide ion is more stable than Phenoxide ion
(b) Phenoxide ion is more stable than Ethoxide ion
(c) Phenol undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction.
(d) Phenol undergoes protonation easily.
Ans. (b)
Which reagent will be required for one step conversion of benzenediazonium chloride to phenol ?
(a) Cu2Cl2 (b) NaOH(aq)
(c) H2O (d) Alcoholic KOH
Ans. (c)
Give equations of the following reactions :
Phenol is treated with conc. HNO3.
Propene is treated with B2H6 followed by H2O2/OH..
![]()
![]()
![]() 3CH3–CH2–CH2–OH
3CH3–CH2–CH2–OH
Sodium t-butoxide is treated with CH3Cl.
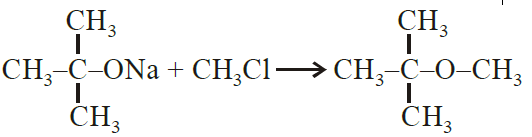
How will you distinguish between butan-1-ol and butan-2-ol ?
On heating with (NaOH + l2), Butan-2-ol forms yellow ppt of iodoform (CH4) whereas
butan-1-ol does not (or any other correct chemical test)
Arrange the following in increasing order of acidity :
Phenol, ethanol, water
(c) Ethanol < Water < Phenol
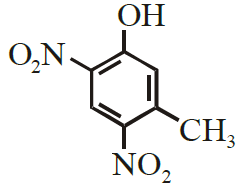
Write the structure of the major product obtained from dinitration of 3-methylphenol.
How would you convert : Phenol to benzoquinone

Boiling point of ethanol is higher than that of dimethyl ether. Why ?
Due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
o-nitrophenol is steam volatile due to intramolecular hydrogen bonding while p-nitrophenol is less volatile due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Anisole on reaction with HI gives phenol and CH3.I as main products and not iodobenzene and CH3OH. Why ?
Weaker (O-CH3) bond and stronger (O-C6H5) bond ,due to resonance / carbon in benzene is sp2 hybridized due to which partial double bond character.
Explain the following observations :
Phenol is more acidic than ethanol.
The phenoxide ion left after the removal of a proton is stabilized by resonance where as alkoxide ion is not which is left after the removal of a proton found alcohol.
o- and p-nitrophenols are more acidic than phenol.
o & p-nitrophenols are more acidic then phenol due to .M effect of NO2 at from o & p
position make the ejections of H+ easity & secondly stabilized the conjugate base.
Write the equations involved in the following reactions:
Reimer . Tiemann reaction

Williamson.s ether synthesis.
Williamson ether synthesis is a laboratory method to prepare symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers by allowing alkyl halides to react with sodium alkoxides.
R -X + R’- O-Na →R -O -R’ + NaX
Alkyl halide Sodium alkoxide Ether
This reaction involves SN2 attack of the alkoxide ion on the alkyl halide. Better results are
obtained in case of primary alkyl halides.
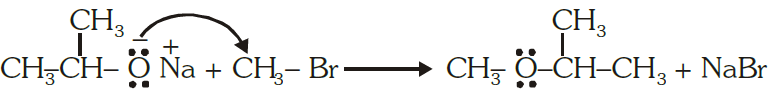
If the alkyl halide is secondary or tertiary, then elimination competes over substitution.
Phenol to salicylaldehyde
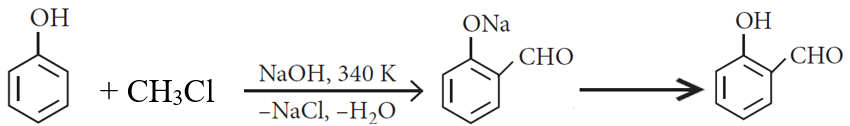
Give reason for the following :
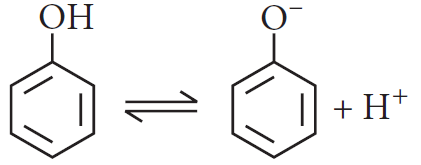
Phenol is more acidic than ethanol.
Phenols are more acidic than alcohols. It can be explained on the basis of that alcohol on losing H+ ions form alkoxide ion and phenol forms phenoxide ion.
The greater acidity of phenol is due to the stability of the phenoxide ion which is resonance stabilized.
On the other hand, alkoxide ion shows no such resonance stabilisation and is unstable.
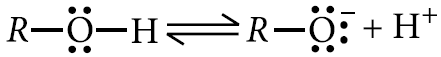
Give a chemical test to distinguish between
2-pentanol and 3-pentanol.
On adding I2 and NaOH, 2-pentanol will give yellow precipitate of iodoform whereas 3-pentanol will not give yellow precipitate.
Ortho-nitrophenol is more acidic than orthomethoxyphenol. Why?
As we know that the electron withdrawing groups enhance the acidic character of phenols because they help in the stabilisation of phenoxide ion by dispersing negative charge. Nitro group is an electron withdrawing group whereas methoxy group destabilise the phenoxide ion by intensifying the negative charge. Thus, o-nitrophenol is more acidic than o-methoxyphenol.
Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(i) Ethanol and phenol
Distinction between ethanol and phenol. FeCl3 test : Phenol gives a violet colouration with
FeCl3 solution while ethanol does not.
3C6H5OH + FeCl3 →(C6H5O)3Fe + 3HCl
(ii) Propanol and 2-methylpropan-2-ol.
On oxidation in presence of acidic KMnO4, 1° alcohol (propanol) will give aldehyde while 3° alcohol (2-methylpropan-2-ol) will give a ketone.
Alcohols are more soluble in water than the hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses.
The solubility of alcohols in water is due to their ability to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. Hydrocarbons cannot form such hydrogen bonds, hence they are insoluble in water.
The boiling point of ethanol is higher than that of methanol.
It is due to higher molecular weight, more surface area, more van der Waals’ forces of attraction in C2H5OH than CH3OH.
Why phenol undergoes electrophilic substitution more easily than benzene?
Phenols undergo electrophilic substitution reaction more easily than benzene due to strong activating effect of –OH group attached to benzene ring.
