👁️ Anatomy of Human Eye: Structure, Function, and Importance
The human eye is a fascinating and complex organ that enables us to perceive the world in vivid detail. This post will explore all major parts of the eye as per NCERT guidelines, using a detailed breakdown of each component and its function.
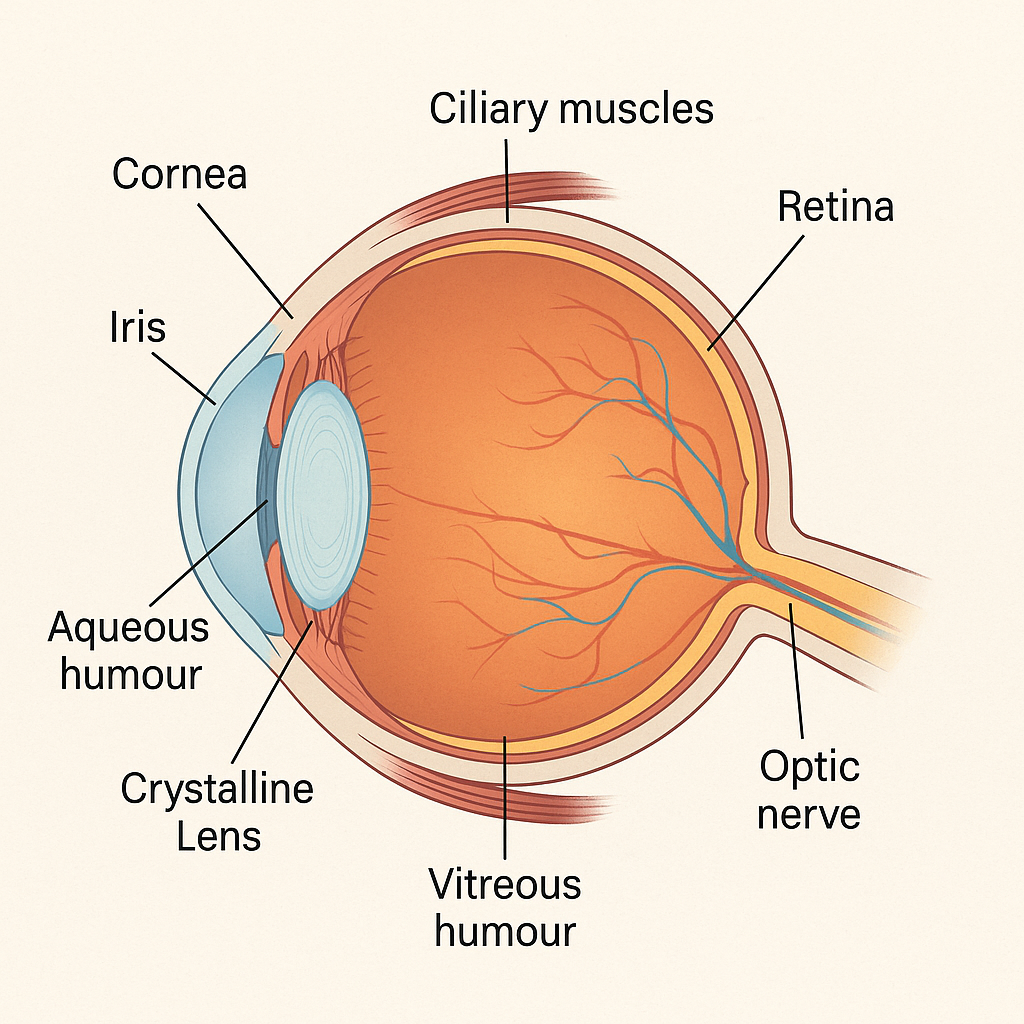
🔍 1. Cornea – The Transparent Front Layer
- The cornea is the transparent, dome-shaped outermost layer of the eye.
- It helps focus incoming light onto the retina.
- Acts as a protective shield against dust, germs, and harmful particles.
🌈 2. Iris – The Colored Part of the Eye
- The iris is the colored part (brown, blue, green) of the eye.
- It controls the size of the pupil, regulating the light entering the eye.
⚫ 3. Pupil – The Eye’s Light Gate
- The pupil is a black circular opening at the center of the iris.
- It expands in dim light and contracts in bright light to regulate light entry.
💧 4. Aqueous Humour – Nourishing Fluid
- A clear, watery fluid found between the cornea and the lens.
- Maintains intraocular pressure and supplies nutrients to the cornea and lens.
🔍 5. Crystalline Lens – The Natural Focus Mechanism
- A transparent, flexible, convex structure located behind the pupil.
- Focuses light onto the retina for clear vision.
💪 6. Ciliary Muscles – The Eye’s Adjusters
- Small muscles that surround the lens.
- They adjust the lens shape to focus on near or distant objects (accommodation).
🔴 7. Vitreous Humour – Gel-Like Support
- A clear, gel-like substance between the lens and retina.
- Helps maintain the shape of the eyeball and supports the retina.
🎯 8. Retina – The Image Processor
- The innermost layer of the eye containing light-sensitive cells (rods and cones).
- Converts light into electrical signals that are sent to the brain.
🔌 9. Optic Nerve – The Brain’s Connection
- A thick bundle of nerve fibers that connects the retina to the brain.
- Transmits visual information for interpretation.
🌐 Summary Table of Eye Components
| Component | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Cornea | Focuses light, protects the eye |
| Iris | Controls pupil size and light entry |
| Pupil | Adjusts light intake |
| Aqueous Humour | Maintains pressure, nourishes eye |
| Crystalline Lens | Focuses light onto the retina |
| Ciliary Muscles | Change lens shape for focus |
| Vitreous Humour | Maintains eye shape and supports retina |
| Retina | Converts light into electrical signals |
| Optic Nerve | Transmits signals to brain |
🧠 How Vision Works – Step-by-Step
- Light enters through the cornea and is refracted.
- It passes through the aqueous humour, pupil, and lens.
- Lens adjusts to focus the light on the retina.
- The retina’s rods and cones detect the light and convert it into electrical impulses.
- Optic nerve carries these signals to the brain where the image is interpreted.
📝 Final Words
The human eye is a miracle of biology, combining precision optics and real-time image processing. Understanding the parts of the eye not only helps in academic learning but also makes us appreciate our sense of sight more deeply. Regular eye checkups, proper lighting, and protective habits can help preserve this gift.
📚 Based on NCERT
