Give reasons for the following
(i) Ethyl iodide undergoes SN2 reaction faster than ethyl bromide
Ans: Iodide is better leaving group because of its larger size than bromide therefore ethyl iodide under goes SN2 reaction faster than ethyl bromide.
(ii) (±) 2-Butanol is optically inactive.
Ans: +2 butanol is a racemic mixture it is a mixture which contains two enatiomers in equal proportion and thus have zero optical rotation so it is optically inactive.
(iii) C-X bond length in halobenzene is smaller than C-X bond length in CH3-X.
Ans: Due to delocalisation of lone pairs of electron of X atom over the benzene ring. C-X bond in halogenzen acquire some double bond character while in CH3-X, C-X bond is a single bond.
(iv) Preparation of ethers by acid dehydration of secondary or tertiary alcohols is not a suitable method. Give reason.
Ans. The formation of ethers by dehydration of alcohol is a bimolecular reaction (SN2) involving the attack of an alcohol molecule on a protonated alcohol molecule. In this method, the alkyl group should be unhindered. In case of secondary or tertiary alcohols, the alkyl group is hindered. As a result, elimination dominates substitution. Hence, in place of ethers, alkenes are formed.
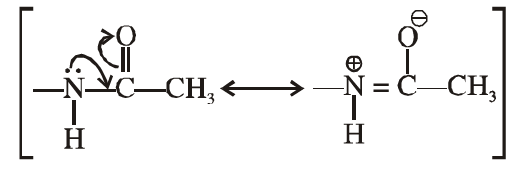
(v) Acetylation of aniline reduces its activation effect.
Ans. Due to the resonance, the electron pair of nitrogen atom gets delocalised towards carbonyl group/ resonating structures.
(vi) CH3NH2 is more basic than C6H5NH2
Ans: Because of +I effect in methylamine electron density at nitrogen increases whereas in aniline resonance takes place and electron density on nitrogen decreases / resonating structures.
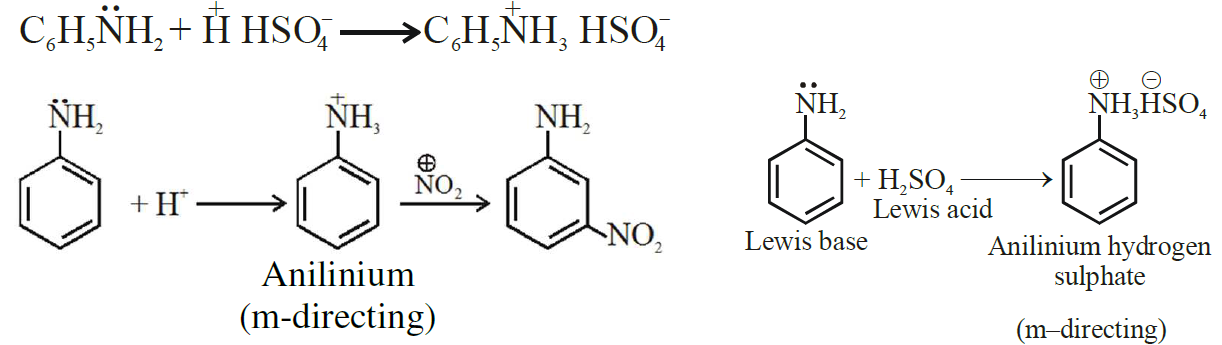
(vii) Although -NH2 is o/p directing group, yet aniline on nitration gives a significant amount of m-nitroaniline.
Ans: Due to protonation of aniline/formation of anilinium ion
(viii) Protonation of Phenols is difficult whereas ethanol easily undergoes protonation.
Ans. In phenols lone pair of electron on oxygen are delocalized over benzene ring due to resonance but in alcohol lone pair of electron on oxygen are localized & hence available for protonation / + R- effect in phenol but not in ethanol.
(ix) Boiling point of ethanol is higher than that of dimethyl ether.
Ans: Due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding
(x) Anisole on reaction with HI gives phenol and CH3-I as main products and not iodobenzene and CH3OH.
Ans: Weaker (O-CH3) bond and stronger(O-C6H5) bond ,due to resonance / carbon in benzene is sp2 hybridized due to which partial double bond character.
(xi) p-nitrophenol is more acidic than p-methylphenol.
Ans. Due to withdrawing effect of -NO2 group & donating effect of -CH3 group or 4-nitrophenoxide ion is more stable than 4-methylphenoxide ion
(xii) Bond length of C-O bond in phenol is shorter than that in methanol.
Ans: Due to +R effect of -OH group in phenol / due to sp2 hybridization of C-atom in C-OH group in phenol whereas sp3 hybridization of C-atom in C-OH group in methanol.
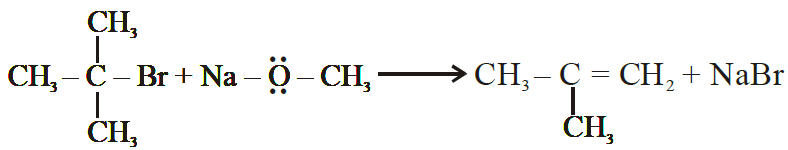
(xiii) (CH3)3C – Br on reaction with sodium methoxide (Na+ –OCH3). Gives alkene as the main product and not an ether.
Ans: Williamon.s synthesis is not applicable for tertiary alkyl halides as they yield alkenes instead of ethers. The reaction of CH3ONa with (CH3)3C-Br gives exclusively 2-methyl propene.
(xiv) Benzoic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid.
Ans. Due to the electron donating inducting effect (+I) by the alkyl group on acetic acid destabilise the conjugate base of acetic acid.
(xv) Methanal is more reactive towards nucleophilic addition reaction than ethanal.
Ans: Aldehyde which is a functional group (CHO) is more reactive due to less steric effect.
(xvi) Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between propanal and propanone.
Ans: Propanal being an aldehyde reduces Fehling’s solutions to a red-brown ppt of Cu2O, but propanone being a keton does not. Propanone being a ketone does not.
Propanal being an aldehye reduces Tollen’s reagent to a silver mirror but propanone being a ketone does not.
(xvii) Ammonolysis of alkyl halides is not a good methods to prepare pure primary amines.
Ans. Ammonolysis of alkyl halides gives primary amine which behaves as a nucleophile and an subsequent reaction with alkyl halide found 2°, 3° amines and finally forms quaternary ammonium salt. which is difficult to separate.
(xviii) Aniline does not give Friedel-Crafts reaction.
Ans: Aniline does not undergo Friedel-Craft reaction due salt formation with aluminium chloride, the Lewis acid, which is used as catalyst. Due to this, N-atom of aniline acquires positive charge and hence, it acts as strong deactivating group for further reaction.
(xix) Although -NH2 group is o/p directing in electrophilic substitution reactions, yet aniline on nitration gives good yield of m-nitroaniline.
Ans:
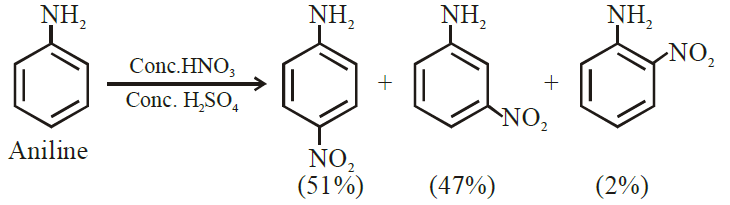
In strongly acidic medium aniline is protonated to form anilinium  ion in which -NH3+ group, + acts as meta directing.
ion in which -NH3+ group, + acts as meta directing.