Define the following term : Molality (m), Molarity (M), Mole fraction
Molality (m) is defined as the number of moles of the solute per kilogram of the solvent and is expressed as :
Molality (m) =![]()
Molarity (M): It is the number of moles of the solute dissolved per litre of the solution. It is denoted by M.
Molarity(M) = ![]()
= ![]()
Mole fraction : Mole fraction is the ratio of number of moles of solute or solvent and total number of moles of solution. It is denoted by x.
![]()
![]()
Differentiate between molarity and molality of a solution. How can we change molality value of a solution into molarity value?
|
Molarity |
Molality |
|
Number of moles of solute dissolved in one litre solution is called molarity. |
Number of moles of solute dissolved in one kg solvent is called molality. |
|
Molarity(M) = = |
Molality (m) = |
|
Molarity depends on temperature as volume depends on temperature. Molarity decreases with rise in temperature. |
Molality is independent of temperature as mass does not change with temperature. |
If MB is the molar mass of solute, d is the density of solution then molality (m) of a solution can be converted to molarity (M) by using the formula,
M = 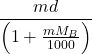
If MB is the molar mass of solute, d is the density of solution then molarity (M) value of a solution can be converted into its molality (m) by using the following formula,
m = ![]()
Why aquatic animals are more comfortable in cold water than in warm water?
Increase in temperature decreases the solubility of oxygen in water. As a result, amount of dissolved oxygen decreases. It becomes more difficult to breathe as oxygen is less. Hence, the aquatic species are not comfortable in warm water.
Explain: Henry’s law about dissolution of a gas in a liquid.
Henry’s law states that, the partial pressure of the gas in vapour phase (p) is proportional to the mole fraction of the gas (x) in the solution. p = KH⋅x where, KH = Henry’s law constant. Different gases have different KH values at the same temperature.
Why is air diluted with helium in the tanks used by scuba divers?
To minimise the painful effects of decompression sickness in deep sea divers, oxygen diluted with less soluble helium gas is used as breathing gas
At higher altitudes people suffer from anoxia resulting in inability to think.
At high altitudes, the partial pressure of oxygen is less than at the ground level. As a result, there is a low concentration of oxygen in the blood and tissues of the people living at high altitudes. Thus, they feel weak and are unable to think properly.
Define Raoult’s law.
Raoult’s law : For a solution of volatile liquids, the partial pressure of each component in the solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction. Thus, for any component, partial vapour pressure, p ∝ x ⇒ p = p.x
where, p° = vapour pressure of pure component
x = mole fraction of that component
Write two differences between ideal solutions and non-ideal solutions.
(i) In ideal solutions, each component obeys Raoult’s law at all temperatures and concentrations whereas in non ideal solutions, they do not obey Raoult’s law.
(ii) In ideal solutions ΔVmixing = 0 and ΔHmix= 0 whereas in non ideal solutions, ΔVmix ≠ 0 and ΔHmix ≠ 0.
Define the terms osmosis and osmotic pressure. Is the osmotic pressure of a solution a colligative property? Explain.
Osmosis : The spontaneous movement of the
solvent molecules from the pure solvent or from a
dilute solution to a concentrated solution through
a semi-permeable membrane is called osmosis.
Osmotic Pressure : The minimum excess pressure
that has to be applied on the solution to prevent the passage of solvent molecules into it through
semipermeable membrane is called osmotic
pressure.
Osmotic pressure is a colligative property because
it depends on the number of solute particles and
not on their nature.
Define the following term :
van’t Hoff factor
van’t Hoff factor : It is defined as the ratio
of the experimental value of colligative property
to the calculated value of the colligative property
and is used to find out the extent of dissociation or
association. Mathematically, it is represented as.
![]()
Define the following term :
Abnormal molar mass
The molar mass which is either lower or
higher than the expected or normal value is
known as abnormal molar mass.
