what are reducing sugars?
Carbohydrates which reduce Fehling solution to red precipitate of cuprous oxide or Tollen”s Reagent to Metallic silver are called reducing sugars .all and disaccharides except sucrose are reducing sugars.
Carbohydrates which on hydrolysis give 2 to10 molecules of monosaccharides are called Oligosaccharides for example sucrose.
Define the denaturation of proteins.
Due to physical and chemical change hydrogen bonds in proteins are disturbed. By this globules unfold and helix gets uncoiled therefore proteins losses its biological activity this is known as denaturation of proteins.
Which one of the following is a disaccharide: starch, maltose, fructose, glucose?
Maltose
Write the name of the linkage joining two nucleotides.
Phospho diester linkage
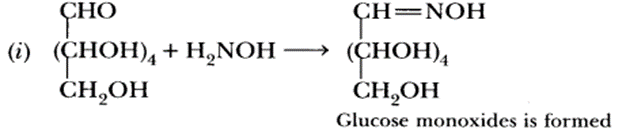
Write the product obtained when D-glucose reacts with H2N—OH
Amino acids show amphoteric behavior why?
Amino acids show amphoteric behavior because they have acidic as well as basic group
Write the product obtained when D-glucose reacts with Br2 water.
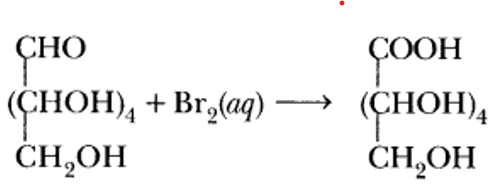
What are biocatalysts? Give an example
Those catalysts which catalyze biochemical reactions are called biocatalysts e.g. invertase catalyzes hydrolysis of cane-sugar to form glucose and fructose.
State what you understand by primary structure and secondary structure of proteins
Primary structure of protein: The sequence in which the amino acids are arranged in a protein is called the primary structure of protein.
Secondary structure of protein: The polypeptide chain gets folded due to intramolecular hydrogen bonding between the carboxyl and amino groups. In an a-helix, the peptide chain coils and the turns of the coil are held together by hydrogen bonds. Another type of secondary structure is possible in which the protein chains are stretched out. This is the P-pleated sheet structure.
“The two strands of DNA are not identical but are complementary.” Explain.
DNA consists of two strands of polynucleotides coiled around each other in the form of a double helix. The nucleotides making up each strand of DNA are connected by phosphodiester bonds. This forms the backbone of each DNA strand from which the bases extend. The bases of one strand of DNA are paired with bases on the other strand by means of hydrogen bonding. This hydrogen bonding is very specific as the structures of bases permit only one mode of pairing. Adenine pairs only thymine through two hydrogen bonds and guanine pairs with cytosine through three hydrogen bonds. The two strands of DNA are said to be complementary to each other in the sense that the sequence of bases in one strand automatically determines that of the other. These strands are not identical but complementary.
State. what do you understand by primary structure and secondary structure of proteins.?
Primary structure of protein: The sequence in which the amino acids are arranged in a protein is called the primary structure of protein.
Secondary structure of protein: The polypeptide chain gets folded due to intramolecular hydrogen bonding between the carboxyl and amino groups. In an a-helix, the peptide chain coils, and the turns of the coil are held together by hydrogen bonds. Another type of secondary structure is possible in which pleated sheet structure.
